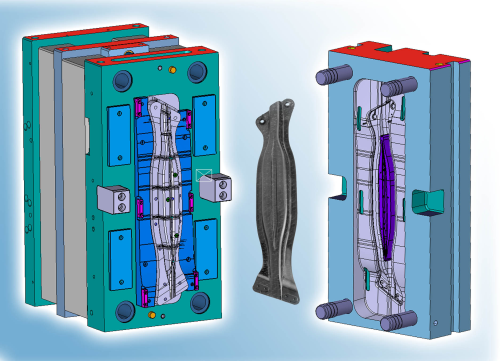
The GK LIPfibre (Georg Kaufmann Lightweight Integrated Process fibre) moulding technology combines a thermoforming and injection mould to produce lightweight structural components from glass fibre reinforced thermoplastics.
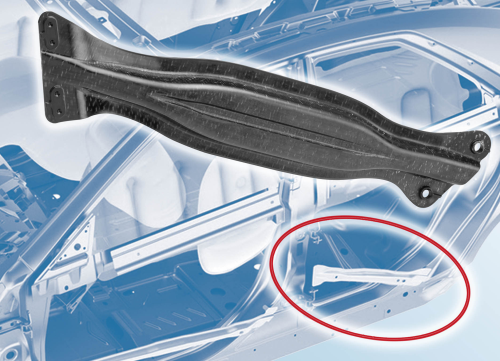
At the K 2010 plastics exhibition in Germany in November, Georg Kaufmann demonstrated the production of a passenger car side impact protection component on an injection moulding machine from KraussMaffei. The project was realised in collaboration with Audi AG, KraussMaffei Technologies GmbH, Lanxess Deutschland GmbH, Bond-Laminates GmbH, and Jacob Composite GmbH. For the production of this impact modifier, a flat pre-heated sheet of fabric and glass fibre reinforced thermoplastic is first thermoformed and remains in the now closed mould. Then in a second step, in the same mould, it is enhanced by adding reinforcement ribs, corners and edges. The material for the ribs is a glass fibre filled polymer.
This combination of thermoforming and injection moulding requires a production system in which the individual process steps are exactly coordinated and synchronised with each other, in order to guarantee the required product quality and process reliability, explains Georg Kaufmann. The first stage of the process – the thermoforming of the glass fibre reinforced thermoplastic sheet – begins with a special cavity insert that presses the sheet onto the core and holds it in place. During thermoforming the sheet cannot develop any creases. The orientation of the fibres in the now formed sheet is also important and this is predetermined according to the functionality of the part.
The mould remains in its closed position at the end of the thermoforming process. The melt for the overmoulded ribs, consisting of a glass fibre reinforced polymer, is injected via a hot runner system and bonds completely with the thermoformed sheet. In addition the melt flow ensures that all sections of the part are fully formed and filled.
The research production mould was equipped with several sensors for pressure and temperature measurements. These monitored the various process stages, the shaping of the glass fibre reinforced sheet during thermoforming, the injection of the polymer melt, and the complete filling of all corners and edges of the part. These measurements will help to better understand the requirements for future applications.
Georg Kaufmann, headquartered in Busslingen, Switzerland, specialises in mould making and related technologies for the automotive industry.




