The first two grades are designated Ultramid B3ZG7 CR and Ultramid B3ZG3 CR and are reinforced with 35% and 15% glass fibres respectively.
The third product, Ultramid B3ZG10 CR, is the first impact-modified polyamide 6 from BASF with 50% glass fibres.
BASF notes that although initially targeted for body applications intended to provide pedestrian protection, these thermoplastic composites are also suitable for other crash-relevant components on or in the vehicle – wherever fast absorption of high amounts of energy is required.
The three products were developed as a modular system with custom-tailored properties and, depending on requirements, offer the customer a somewhat softer or stiffer version.
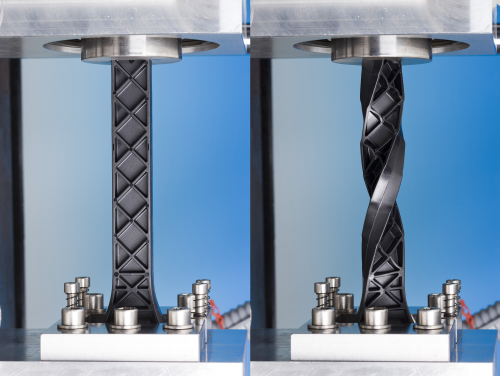
Twisted Eiffel Tower test
For development and testing purposes, BASF developed a bending and torsion test specimen specifically for these new crash-optimised grades.
The test specimen is reminiscent of the Eiffel Tower in Paris and has 45° ribbing. While the previous CR material Ultramid B3WG6 CR can already be distorted by almost 150° in static torsion tests without breaking, the new grades withstand distortion by up to 240° without being damaged.
The part on which these tests were performed was optimised in view of load-bearing by means of BASF's ULTRASIM™ simulation.
Using this test specimen, BASF can perform single-point and three-point bending tests in addition to the torsion test.





