


Electric-mobility, carbon dioxide (CO2) emission limits, gasoline and energy prices – these are some of the factors driving lightweight automotive design. Lightweight design requires suitable, economic manufacturing technologies in addition to the use of lightweight materials.
Large, high-strength structures are currently being manufactured in the aerospace industry using the resin transfer moulding (RTM) process – however, in very low quantities and sometimes with a high percentage of manual work. In automotive manufacture, parts produced with the RTM process are predominantly used for reasons of visual appearance and built into premium class vehicles in small quantities. Fibre reinforced plastics (FRP) will only be more widely used in automotive manufacture for high-strength load-bearing structures if reliable, automated RTM production lines for series production are developed.
German processing machinery specialists Dieffenbacher and KraussMaffei are cooperating in the field of RTM and have responded to market requirements by developing an automated production line for the high-pressure RTM (HP-RTM) process. This production system includes units for preform manufacture, the pressing process and the finishing processes. HP-RTM results in shorter injection times, improved impregnation of the preform and leads to shorter cycle times than the traditional RTM process.
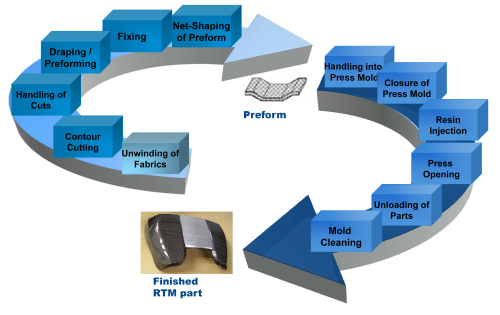
Preform manufacture
For the production of HP-RTM components, a preform made of a textile reinforcement material is required. Such preforms are manufactured in the Dieffenbacher preform centre, typically using a fully automated process.
Limp technical textiles in the form of fabrics or mats made from carbon and/or glass fibres are unreeled from a roll on to a cutting machine. Using CNC cutting technology, the plies are cut to size as required for the component to be produced. This is done using cutting programs generated from existing CAD component data. The cut plies are joined to form a layered package and subsequently fed into the forming unit, which is referred to as the draping station.
Robots can be used to ensure reliable handling of the cut fabric/mat and the consolidated preform. The preform centre can be operated as a standalone unit or in line with the press process.
The press process
The preform manufacturing process is followed by the press process, which involves impregnation of the preform with an epoxy resin system and then curing.
After the consolidated preform is placed into the RTM mould by a robot, a hydraulic Dieffenbacher press performs the actual pressing process with a press force of up to 36 000 kN (3600 tonnes), depending on the internal mould pressure as well as the size and complexity of the component. A buffer drive makes it possible to achieve slide closing speeds of up to 450 mm/s (190 inches/min) and pressing speeds of up to 40 mm/s (17 inches/min) at a short pressure build-up time. The Dieffenbacher short stroke system ensures that the press has particularly high energy efficiency, especially with short forming travels and large slide strokes. An increase in energy efficiency of up to 50% is possible compared with conventional press technology.
The press control system permits different operating programs and optimisation of the cycle times. Production bolsters entering and leaving the press cyclically permit short mould change times, loading and unloading processes, as well as cleaning of the lower mould half in the off-line position.
Improved component quality can be achieved by recompression after completion of the high-pressure injection process.
The injection process
The low-viscosity reaction mixture is injected into the closed mould and the preform package is impregnated. KraussMaffei’s dispensing technology permits an application volume from 10-200 g/s, depending on the resin system and according to the component size required and the process design. The individual resin and hardener components are metered at a high precision in a closed loop process and mixed under high pressure to produce the reaction mixture.
High-pressure metering results in shorter injection times and improved impregnation of the preform and makes it possible to process resin systems with shorter curing times. This leads to shorter cycle times and increased cost effectiveness. Moreover, this offers additional advantages such as a lower porosity while maintaining a high surface quality. Highly precise temperature control makes it possible to further optimise the cycle time and benefit from the advantages of special RTM resin systems.
Using a KraussMaffei high-pressure mixing head eliminates cost-intensive off-line times and special materials for cleaning conventional low-pressure mixing heads. It is self-cleaning and therefore particularly cost-effective for large production volumes, which has already been proven by various series production applications.
Additional release agent supply blocks make it possible to feed mould release agent required for the process directly to the compact self-cleaning KraussMaffei high-pressure mixing head with a high accuracy and process reliability even at minimum quantities (e.g. 0.1 g/sec). Highly precise and reproducible release agent metering is absolutely necessary for reliable implementation of downstream processes.
Finishing
Finishing is one of the final steps in the process chain. It involves shaping the final contour of the component and adding, for example, mounting holes and openings for inserts. Finishing by milling is performed by tailor-made complete solutions developed by KraussMaffei. Either automated cutting booths or portable cutters may be used, depending on the size and complexity of the components. Robots take care of component handling between the process steps.
Turnkey HP-RTM plants
Cooperation between Dieffenbacher and KraussMaffei, as well as the Fraunhofer Institute for Chemical Technology (ICT) and the LCC Munich (Carbon Faculty), make the worldwide delivery of turnkey facilities for the HP-RTM process from a single source possible. The innovative HP-RTM line developed by these partners includes the following features:
- high productivity;
- consistently high degree of automation;
- short cycle times;
- automated preform manufacture;
- energy-efficient press technology;
- self-cleaning high-pressure mixing heads;
- elimination of auxiliary materials in both preform manufacture and injection process; and
- low porosity while maintaining excellent surface qualities.
An important element of the cooperation is the future development of a sustainable HP-RTM process technology and the further development of integrated HP-RTM lines. In order to promote this technology, the Fraunhofer ICT has been equipped with an RTM cell consisting of a Dieffenbacher press and a KraussMaffei HP-RTM mixing and metering unit (RimStar Thermo). This facility is used for both internal tests and customer experiments.
The success of these developments is highlighted by laboratory and series equipment already delivered to renowned manufacturers including Benteler SGL, Fritzmeier, BMW, Audi and Daimler. ♦
This article was published in the September/October 2011 issue of Reinforced Plastics magazine. To appy to receive your copy of the magazine please complete the subscription form. (The digital edition of Reinforced Plastics magazine is distributed free of charge to readers who meet our qualifying criteria.)






