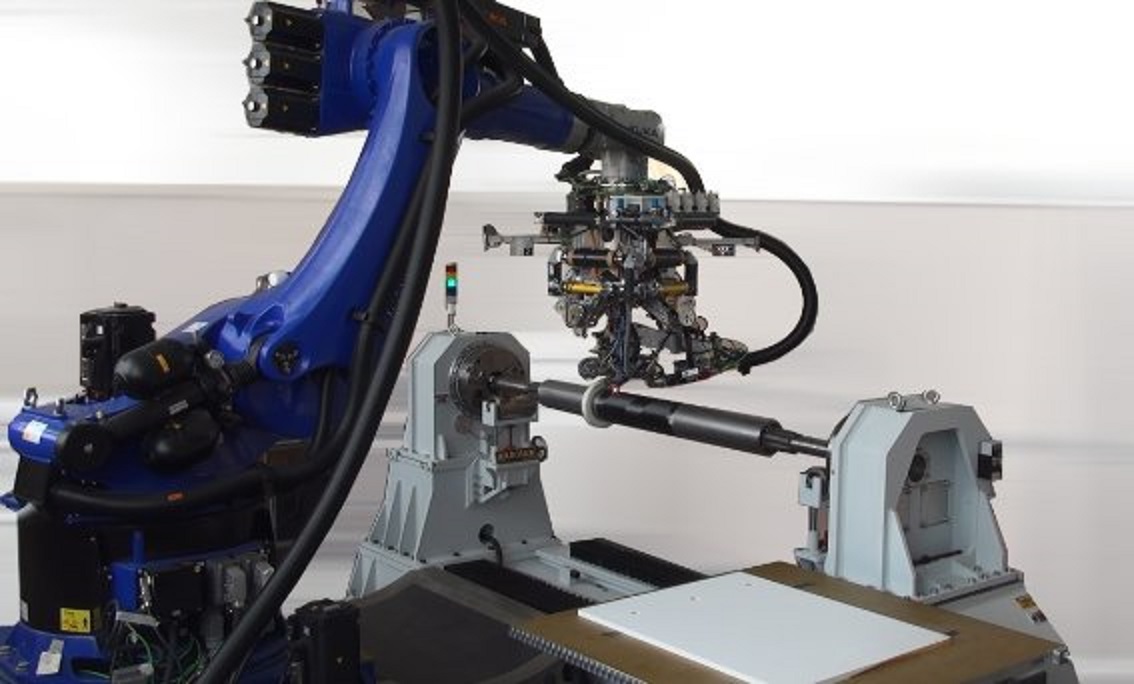
Mikrosam, a supplier of composite manufacturing systems based in Macedonia, has reportedly developed a multi-material capable automated fiber placement (AFP) system for Brandenburg University of Technology, Cottbus, Germany.
The company says that the AFP machine has eight axes and can carry out automated placement of thermoplastic fibers, thermoset prepregs, and dry fiber material.
The machine will reportedly allow the department of lightweight design and structural materials at the university to design and test complex 3D parts made of composite materials with structured functional surfaces as required in industries such as aerospace and automotive. The system features an AFP head with uni and bidirectional placement on open 3D shapes and closed mandrel surfaces, such as pipes and vessels.
For thermoplastic composites the system features a laser heating source, temperature control, and a closed-loop process. The dry fiber placement capability on the same AFP head opens possibilities for developing and testing new pre-forms for aerospace and automotive needs, Mikrosam says.
This story is reprinted from material from Mikrosam, with editorial changes made by Materials Today. The views expressed in this article do not necessarily represent those of Elsevier.





