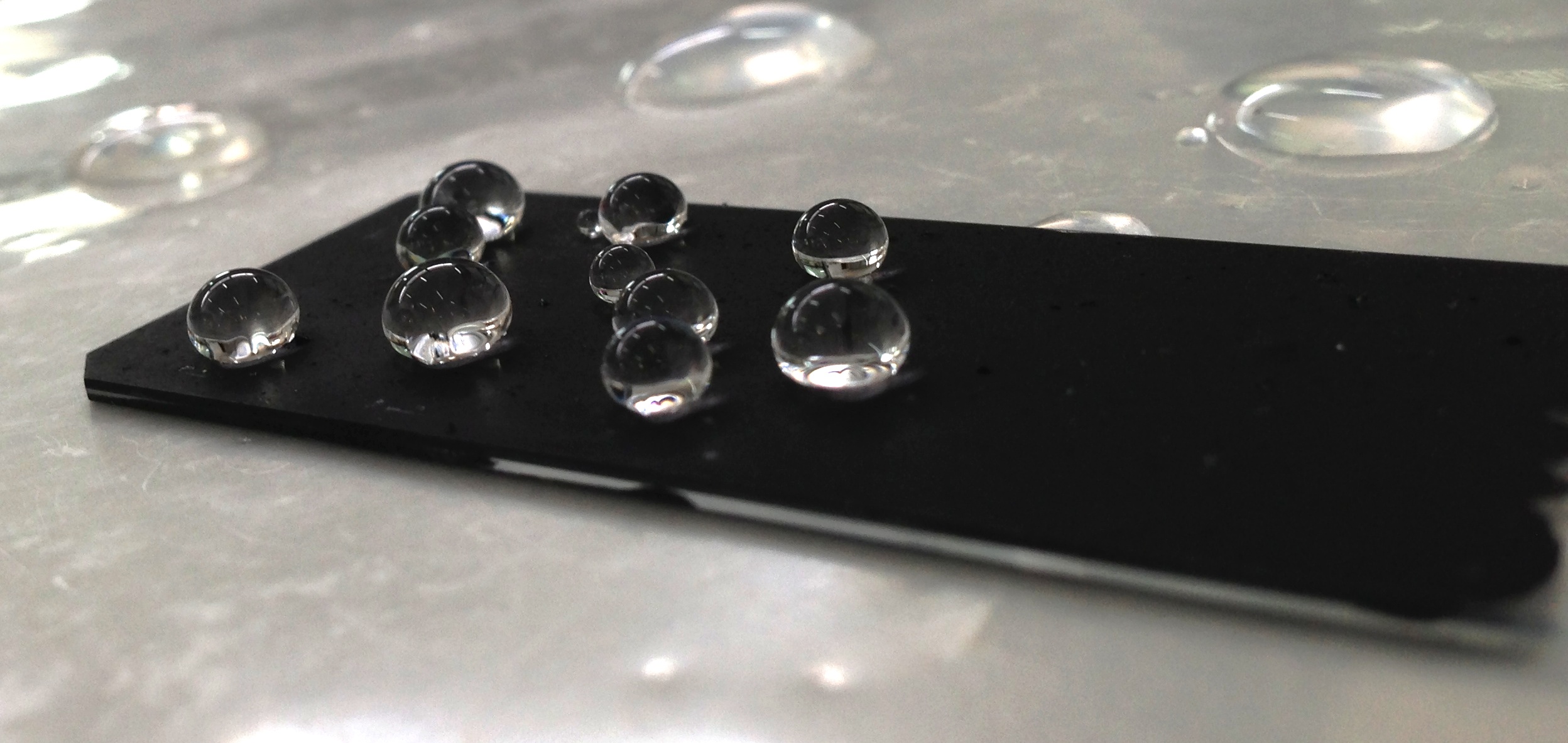
Five technology centers, coordinated by AIMPLAS, have developed new coatings for plastics, wood, metal, ceramics and glass.
AIMPLAS, the Spanish plastics technology center, has completed research reportedly conducted to develop new functional coatings for plastic, ceramics, metal and glass using nanotechnology.
According to the researchers involved in the project, nanotechnology applied to the modification of different surfaces is an important tool since many of the right properties or the requirements demanded in a material depend mainly on the surface.
During the project the researchers studied nanomaterials with higher current technology interest, both for polymeric substrates and metallic, wooden, textile, ceramic or in glass substrates. The aim was to find and define common points, synergies and convergences between the different coating technologies and surface treatments. It was important to find surface activation methodologies that could be compatible between metals, woods, textiles, ceramic materials and polymers.
Detecting convergences
Another point of special interest focused on detecting convergences when employing the characterization techniques common in metals, wood, textiles, ceramics or polymers that determine the properties improvement in surface (tribological, sensorial, microbial, different functions, etc).
The research tasks carried out within the frame of the project Nanosurf, funded by the Valencian Centre of Business Competitiveness (IVACE) through the European Regional Development Fund (FEDER) funds, have been coordinated by AIMPLAS with participation by Ceramics Technology Institute (ITC), the Metal Mechanic Technology Institute (AIMME), the Technology Institute of Furniture, Wood and Packaging (AIDIMA) and the Textile Industry Research Association (AITEX).
This story is reprinted from material from AIMPLAS, with editorial changes made by Materials Today. The views expressed in this article do not necessarily represent those of Elsevier.





