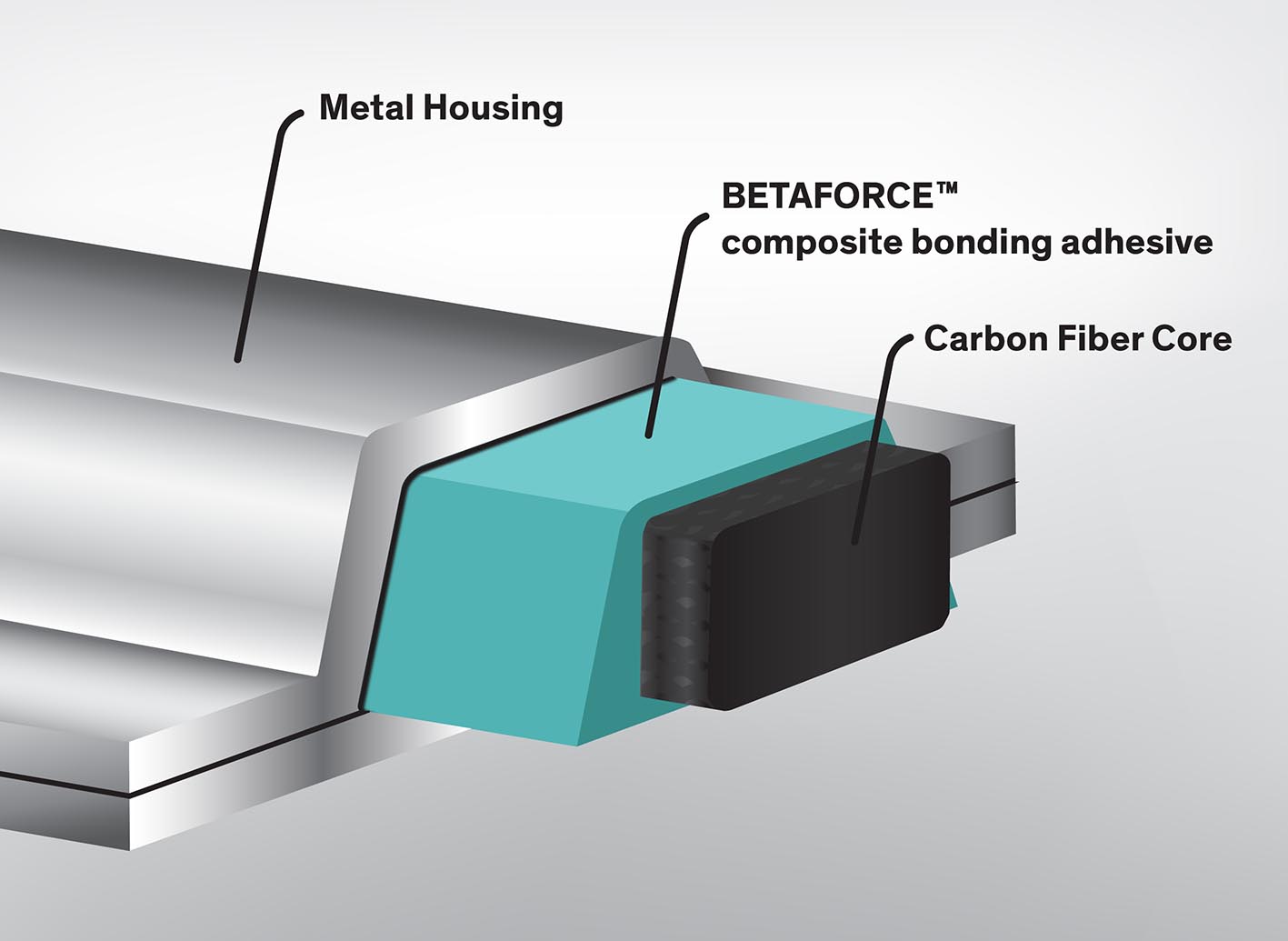
Dow Automotive Systems has introduced a new injection bonding technique for its Betaforce composite bonding adhesives.
The company can now adjust individual parameters to address specific customer requirements for production, such as open times and cycle times, without affecting mechanical properties, Dow says. The can also enable the wider application of carbon-fiber parts in mixed-material assembly and support manufacturers’ lightweight strategies.
Injection bonding is used to bond carbon fiber parts to metal in side-frame applications along the roof. The carbon fiber part can be used as an inlay in a metal housing running along the A-pillar into the roof and down the D-pillar. This helps ensure the stability of the passenger compartment in the case of a side-pole impact or rollover, as well as increasing vehicle torsional stiffness while improving subsequent ride-handling and NVH at the lowest mass. The challenge of integrating such long carbon-fiber composite parts is the management of the differential Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion (CLTE) along the assembly as well as during the operative life of the vehicle.
This story uses material from Dow, with editorial changes made by Materials Today. The views expressed in this article do not necessarily represent those of Elsevier.



