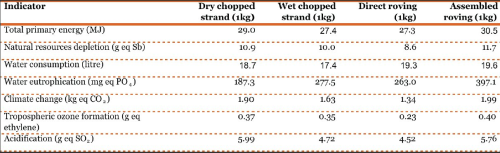
The report covers rovings (assembled and direct) and chopped strands (dry and wet). These continuous filament glass fibre products represent the majority of the reinforcement used in thermosetting and thermoplastic composites applications.
The report was completed according to ISO 14040 and ISO 14044. It has been peer reviewed and accepted at the publicly available European Life Cycle Database (ELCD) operated by the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre.
Results show that most of the energy consumption, depletion of non-renewable resources, increase of greenhouse gas emissions, and acidification come from the glass melting stage that is common to all the products. By contrast, downstream process stages, where products are adapted to customer requirements (e.g. sizing, winding, chopping) play a limited role in the LCA results.
“The European glass fibre industry has a long history of providing efficient glass fibre products to the whole composites value chain by delivering energy-efficient solutions that help reduce greenhouse gas emissions through lightweight, strength and durability,” says Axel Jorns, Secretary General of GlassFibreEurope, the Brussels based association representing glass fibre producers in Europe.
GlassFibreEurope member companies hope that this report will enhance the use of LCA methodology through the value chain and further demonstrate the advantages of using composites versus traditional materials as sustainable solutions.
GlassFibreEuropels members are Cam Elyaf, Johns Manville, Lanxess, Owens Corning, P+D Glasseiden, PPG Industries Fiber Glass, Saint-Gobain Adfors, and 3B.
The LCA report is available on the association’s website.

